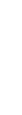Individual response to Hyperemesis Gravidarum (HG) medication varies due to many factors including genetics and hydration. If a patient is vomiting constantly, oral dosing of medications will likely be ineffective and alternates such as sublingual, transdermal (patch/cream), subcutaneous (subQ), intravenous (IV), or other routes should be considered along with hydration. The medication levels for HG are explained below.
Medication Levels for HG
1st Level Medications for HG
- Antihistamine
- Acid reducers
- Vitamins B1 and B6
- Meds successful in previous pg
2nd Level Medications for HG
- Prokinetics: Reglan* (oral, low dose 5 mg)
- Acid blockers/PPIs (e.g. Protonix, Prevacid)
- Serotonin antagonists (e.g. ondansetron/Zofran, granisetron/Kytril)
- Phenothiazines (e.g. Stemetil, Promethazine)
- Corticosteroids (after 8 weeks)
- IV fluid/Nutritional therapy
*prophylax with antihistamine
3rd Level or Experimental Medications for HG
- Benzodiazepine (e.g. Diazepam)
- Neuroleptic (e.g. Inapsine)
- Remeron (Mirtazipine)
- Anticonvulsants (e.g. Neurontin/Gabapentin)
- THC/marijuana (or dronabinol Rx)
- Clonidine (transdermal)
Weaning Medications for HG
Stopping medication quickly can make a patient sicker, so weaning slowly is recommended. Also, adding one medication at a time can show which one is helping symptoms.
GET INVOLVED
- Participate in HG research.
- Become an advocate.
- Make a gift to the HER Foundation.
- Share your story and support other HG moms.
- Become a HER Foundation volunteer.
- Blog about HG and show support for HER.
- Share resources with local health professionals and hospitals.
©2020 HER Foundation. All rights reserved.
Posted in HG Management, What is HG