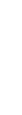Hyperemesis Gravidarum (HG) Management Protocol
Effective HG treatment requires medications and often IV fluids. Download the HER Foundation HG Treatment Protocols and Treatment Algorithm in PDF format for an excellent reference to managing hyperemesis gravidarum (HG) and preventing HG complications. You may download these for personal and professional use as long as you do not change the content and do retain the HER Foundation logos for copyright.
Download HG Management Tools
REHYDRATE METHODICALLY
Banana Bag + Vit B6 + Vit B1
NS or LR + 1 ampule MVI + Vit B6 + Vit B1
NS or Lactated Ringers + 1 ampule MVI + Vit B6 + Vit B1
- • Add prn: KCl, Na, Vit K, Vit D, Zn, Se, Fe, Mg & Ca.
- • Always give 200 mg B1 with glucose to prevent WE.
- • Correct electrolytes slowly to prevent CPM.
- • Restrict PO intake for 24-48 hours for gut rest.
- • Consider midline or central line for frequent IVs
IMPLEMENT COMPASSIONATE CARE
Women with HG are miserable for months and their concerns and requests should be taken seriously. Every possible comfort measure should be taken to minimize unnecessary suffering. Compassionate and effective treatment prevents therapeutic termination, and influences if she and baby will suffer from physical and psychological complications (e.g. trauma, organ damage) during pregnancy and long-term.
PRESCRIBE ANTIEMETIC MEDICATIONS for HG
Choose a drug targeting the main triggers (e.g. motion). If numerous triggers, and/or more severe symptoms, consider serotonin antagonists. Multiple meds may be needed simultaneously throughout pregnancy. Be proactive and aggressive early in pregnancy if she has a history of HG. See the most common medications for HG and strategies to improve response.
PREVENT OR TREAT ADDITIONAL ISSUES
Both HG and the treatments for HG can cause additional issues. Proactive prevention and treatment of these can reduce HG severity.
Issues: ptyalism, GERD, encephalopathy, gastroparesis, UTI, insomnia, h-pylori, cholestasis, debility, embolus.
Medication side effects: severe constipation, serotonin syndrome, anxiety, headache, extrapyramidal symptoms.
INPATIENT CARE
- Weigh every 1-2 days
- Use comfort measures
- Rehydrate: IV Fluids + MVI + B complex/thiamin IV + electrolytes (treat mild deficiency)
- Consider midline or central/PICC line
- Begin Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition
- Labs: Nutritional panel, electrolytes, urinalysis
- Consults: Nutrition, PT, GI, home health, IV team
- D/C: Intake >1 meal/day + adequate fluid intake OR nutritional therapy + no ketones; maintaining or gaining weight
HOME CARE
- Weigh Monday/Wednesday/Friday
- Complete HELP Score daily
- Daily Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition OR
- IV Fluids + MVI + B complex/thiamin IV & electrolytes
- Weekly Labs if TPN: CMP, electrolytes
- D/C: Intake ≥ 2 meals/day + adequate oral fluids
+ no ketones
(CMP=comprehensive metabolic panel)
OUTPATIENT CARE
FIRST VISIT
- Establish compassionate rapport
- R/O other causes of HG: hydatiform mole (GTD), gall bladder & pancreatic disease, helicobacter pylori, hyperthyroidism
- Labs: Urinalysis, hormone levels, comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), thyroid panel
EACH VISIT
- Assess with HELP Score & HER Assessment Tools
- Try prenatal with food or iron-free as tolerated
- Weigh at least weekly & trend % weight loss
- Labs prn dehydration: electrolytes, CMP, u/a, ketones
- Encourage active oral care (e.g. water flosser) & eval
- Evaluate & treat additional symptoms (see above)
- Check WE signs (esp. if infusing glucose)
- Refer for consults & adjunctive care
- Diet: Encourage healthiest food tolerated, add thiamin 50 mg PO BID/TID especially if high carbohydrate diet
- Review medications for tolerance/side-effects Monitor thiamin & vitamin K & electrolyte needs
2nd & 3rd TRIMESTER
- Labs: thyroid panel, iron, CMP
- PT consult: weakness/atrophy, birth prep
- Use alternate for Glucola (GTT), e.g. jelly beans, juice
ANTIEMETIC ESSENTIALS
There are many strategies to optimize HG treatment. HER Foundation has developed essential practice tools for HG care.
- 1st: change dose/frequency
- 2nd: change route (SubQ, TD, compound, rectal, vaginal)
- 3rd: Add/replace a medication
Key Practices for Medications
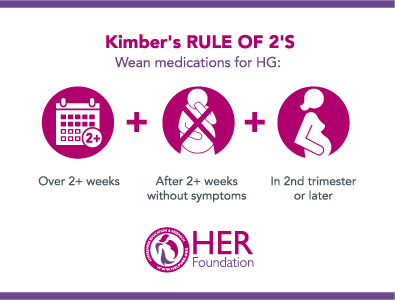
- Avoid abrupt changes in 1st trimester
- Wean over 2+ weeks if asymptomatic
- Prevent/proactively treat side-effects
- Cocktail: 1st level meds + 5HT3 antagonist + metoclopramide or promethazine
1ST LEVEL MEDS
- Antihistamine
- Acid reducers
- Vitamins B1 & B6 50-100 mg/day
- Rx’s successful in previous pg
2ND LEVEL MEDS
- Prokinetics (Reglan (Metoclopramide* 5-10 mg QID)
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPI)
- Serotonin antagonists (ondansetron 8 mg QID or 4 mg every 3 hours, granisetron 2 mg BID or TD)
- Promethazine* (Phenergan 25mg QID)
- Methylprednisolone (after 8 weeks)
- IV fluids/Nutritional therapy
3RD LEVEL MEDS/EXPERIMENTAL
- Phenothiazines* (e.g. chlorpromazine, prochlorperazine)
- Benzodiazepine (e.g. Diazepam)
- Neuroleptic (e.g. Inapsine)
- Remeron (Mirtazapine)
- Anticonvulsants (e.g. Neurontin)
- Marijuana (or Dronabinol Rx)
- Clonidine (Transdermal)
* Prophylax with antihistamines for anxiety; monitor for extrapyramidal symptoms & neuroleptic malignant syndrome
UTILIZE HER FOUNDATION RESOURCES
- Share HER Foundation brochures and Assess & Treat Packets with caregivers and clinicians.
- Share support and survival information with family and friends.
- Use the HELP Score and Assess & Treat Packets, plus HER Clinical Tools.
Post on social media about HER Foundation Resources
- HER Foundation has excellent hyperemesis gravidarum (HG) assessment and treatment tools to help clinicians manage HG!
- Find out all about diagnosing and treating Hyperemesis Gravidarum.
- Get help managing Hyperemesis Gravidarum (HG) at HER Foundation.
WE/ODS ESSENTIALS
Find out more about Wernicke's encephalopathy and Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome, complications of HG.
- Causes: Thiamin & electrolyte deficiency/shifts, infection, diuretics
- Signs: Change in vision or speech or gait or mental status, abdominal pain, headache, cardiac symptoms, somnolence, dizziness, weakness, aphasia, tremor, irritability, spastic paresis, seizure, myalgia, myoclonus, anorexia, dysphagia, elevated transaminase
- Prevention: oral/IV thiamin ≥ 50 mg 1-3x daily; continue postpartum
- Acute Care: Thiamin 100 mg IV up to 1000 mg/day until asymptomatic
- Diagnosis: MRI
- Result: Maternal & fetal morbidity
(pre-eclampsia, SIDS), or mortality - Onset: acute (e.g. IV glucose or electrolytes) or gradual/chronic
WE=Wernicke’s encephalopathy
ODS=Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome
TPN/TPPN ESSENTIALS
- Prevent Refeeding Syndrome
- Add intravenous MVI + folic acid + B Complex + Phosphorus + Mg + Vit D & K + Ca
- Labs/CMP weekly
- Strict adherence aseptic technique & management protocol
- Red flags: chest pain, shortness of breath, temp ≥ 101 F (38.3 C) or ≤ 96.8 F (36 C), redness/swelling/rash
ENTERAL ESSENTIALS
- Prevent Refeeding Syndrome
- Check vitamin K & thiamin dose
- NG/NJ: Use pediatric tube; slow rate
- May need extra IV or fluid boluses
COMFORT MEASURES
- Private room (avoid stimuli)
- Avoid IM injections (atrophy)
- Warm IV fluids/blankets
- Use anesthetic before IVs
- Midline/PICC vs. peripheral IV’s
- Offer preferred foods when least ill
CONSULTS/ADJUNCTIVE CARE
- Consults: GI, nutrition, home health, psychology (PTSD), perinatology/MFM
- Adjunctive care: hypnosis, acupuncture, homeopathy, osteopathic adjustment
PATIENT/FAMILY EDUCATION
- Daily: HELP Score, ketostix
- Call if significant change in HELP Score
- Coping for psychosocial & debility
- Red flag signs: bloody vomit, rapid weight loss, change in breathing or gait or vision or mental status, fever, chills, chest pain/arrhythmia, drowsiness, small amounts of urine, fainting, severe pain
HG FACTS
- Genetic links to IGFBP7 & GDF15 & PGR & RYR2 (cyclic vomiting syndrome)
- Diagnosis: dehydration, poor nutrition, weight loss, debility
- Fetal loss rate: 34%
- Termination rate: 15%
- Maternal Complications: atrophy, esophageal tear/rupture, organ rupture/failure, deconditioning, pneumomediastinum, gall bladder dysfunction, fatty liver, neurological disease, retinal hemorrhage, GI ulcer, premature labor & delivery, PTSD, rhabdomyolysis, severe dental damage, death
- Child Outcomes: IUGR; sensory, emotional, neurodevelopmental, and behavioral disorders; vitamin K deficient embryopathy; stillbirth