Malnutrition & Dehydration
Does HG cause dehydration and malnutrition in pregnancy?
Nutrition is one of the most prolific topics related to pregnancy, yet when someone has HG, they are told malnutrition will not harm them or their unborn child. Ironically, surgical patients are typically given nutritional therapy within one week of being unable to eat, yet those with HG may go weeks or months nearly starving without nutritional intervention.
Research finds that extreme weight loss (>15% of pre-pregnancy weight) is associated with numerous adverse fetal outcomes such as neurodevelopmental delays. Malnutrition in pregnancy can also lead to serious conditions related to deficiencies such as:
- Vitamin K (Binder's phenotype/embryopathy leading to abnormal fetal skeletal formation and abnormal clotting), and
- Vitamin B1/thiamin (Wernicke's encephalopathy, heart issues).
Aggressive treatment is needed to promote a healthier outcome and avoid preventable complications.
As we unravel the genetics of HG, we learn the same proteins that cause cachexia syndrome are involved in HG. The associated genes also alter appetite and taste perception making intake very difficult.
Kimber MacGibbon, RN
Fear of Malnutrition | Fear of Medication
One of the most difficult challenges with HG is managing nutritional needs. Every book, newspaper, magazine, and friend or family member will tell her repeatedly that she must eat healthy or she will harm her unborn child. The fear of harming her unborn child through lack of nutrition is closely followed by a fear of harming her unborn child with medications.
Some choose termination (elective abortion) rather than possibly face having a child who may have been harmed by malnutrition or medications.
Pregnancy Nutrition
Many nutrients are needed to form the placenta, to increase the size of the uterus and breast tissue, and to create amniotic fluid. A mother's blood volume increases by 25–50%, and more fluids, iron, B vitamins, folic acid, zinc and copper, calcium, magnesium, and proteins are needed to support this new blood. Storage levels of most nutrients must be obtained from the diet as well. A nutritional consult may be helpful both during and after pregnancy to ensure she sufficiently rebuilds her nutrient stores, especially while breastfeeding and before becoming pregnant again.
Food Aversions and Cravings
It is very typical for those with HG to have very strong cravings and aversions that prohibit a well-balanced diet for much of their pregnancies, and these preferences may change frequently until delivery. It may be the smell, texture, appearance or taste that leads to nausea and vomiting.
Triggers
The cause is likely a complex interaction of endocrine (hormone) changes related to pregnancy, nutrient deficiencies, mechanical changes in the body, gastrointestinal dysfunction (e.g. reflux), and changes in neurochemicals. The intensity of cravings and aversions can be very high and trigger repeated bouts of severe nausea and/or vomiting.
Thinking about foods, smelling them, or even just seeing food on the television is enough to trigger vomiting for many. She may crave very specific combinations of food characteristics, such as salty and crunchy, or sweet and soft.
Entering a grocery store, opening the refrigerator, or even contemplating food preparation are usually intolerable for at least the first trimester. There is very strong evidence this is caused by certain genes. This has a significant impact both on her and her family and is not something she can control. Finding foods that meet these criteria are crucial to prevent malnutrition.
Support and Understanding
These issues must be acknowledged, supported, and accepted by her family and care providers. It's impossible to fully understand the unusual dietary preferences of HG unless you have experienced it for yourself. Trying to force other foods that are aversive will typically result in vomiting and greater anxiety for the mother.
With HG, any calorie is a good calorie. Any food a mother can tolerate should be offered as soon as possible.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Hyperemesis
Women with HG may vomit or have severe nausea for months that will leave her exhausted and very depleted. It is imperative that women losing weight rapidly and not responding to medications be given nutritional support to prevent significant nutrient depletion in these women. Vitamins, especially B vitamins, are depleted very quickly and if not replaced can worsen her symptoms or put her at risk for life-threatening neurological disorders like Wernicke's Encephalopathy.
Deficiencies left uncorrected may have numerous adverse effects on the breastfeeding child, such as bleeding and neurodevelopmental disorders, especially if a mother had prolonged HG.
Rehydration
At a minimum, mothers requiring hydration should also receive vitamins and electrolytes. Those who continue to lose over 5-10% of their body weight in the early months should be considered for nutritional support to protect the well-being of both mother and child. These mothers are also at greater risk for complications such as pre-eclampsia, fetal loss, premature delivery, and more severe HG. Studies show that an inadequately nourished fetus may grow and develop more slowly, have chronic disease in later life, experience emotional/behavioral and sensory issues, and more likely be preterm.
Refeeding Syndrome
Patients at Risk for Refeeding Syndrome
- Poor nutritional intake
- Weight loss >15%
- Prolonged IV hydration
- Significant stress
- Electrolyte & nutrient depletion
Weight Loss
Weight loss is influenced in part by genetics, and occurs in most cases of HG unless effective medications and nutritional support are offered early in pregnancy. Weight loss may be rapid until the mother becomes emaciated and her metabolism slows. The more weight a mother loses, the greater the risks to her and her child, and the longer her recovery.
Swelling (Edema)
Edema may develop in some patients due to fluid shifts, low protein intake and refeeding syndrome. Monitor weight changes often until patients are asymptomatic and stable.
WEIGHT LOSS CALCULATOR
Calculate your Percent Weight Change by entering your usual weight and actual (current) weight below.
NOTE: These scales are based on non-pregnant subjects.
* Percent Weight Change = [(Usual Weight - Actual Weight) ÷ (Usual Weight)] x 100
Is your weight loss severe?
No research has established weight loss amounts that are safe during pregnancy. Our research finds that there is significant risk to the baby’s long-term health when a woman’s weight loss exceeds 15% of her pre-pregnancy weight.
Other factors need consideration such as the pre-pregnancy weight, which if low, puts mother and baby at greater risk by weight loss. Conversely, a mother who is overweight prior to pregnancy may be able to lose a little more weight without significant risk, provided she gets adequate essential nutrients like vitamins B1, folic acid, and vitamin K.
According to ASPEN, for non-pregnant women, severe weight loss is >2% in a week or >5% in a month. Severe malnutrition is less than 50% of you needed dietary intake for over a week. Pregnancy is an accelerated state of starvation so women likely qualify sooner. Many women with HG would easily be considered malnourished and should be screened carefully and given nutritional intervention.
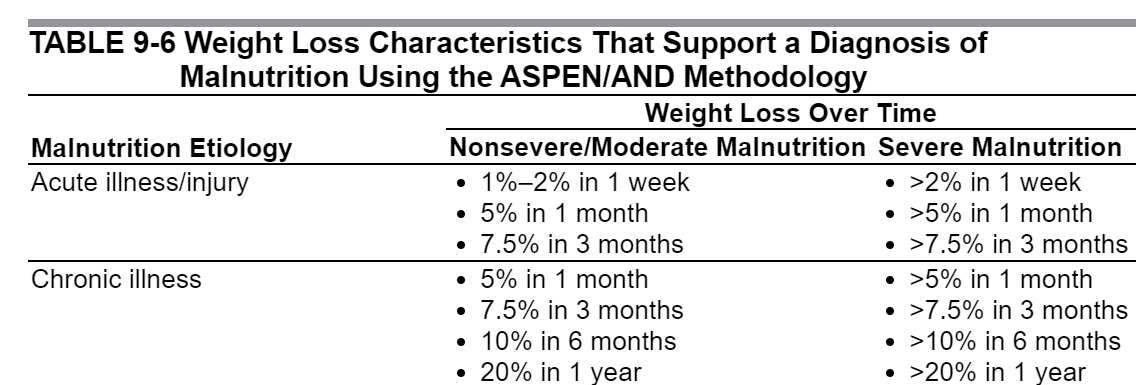
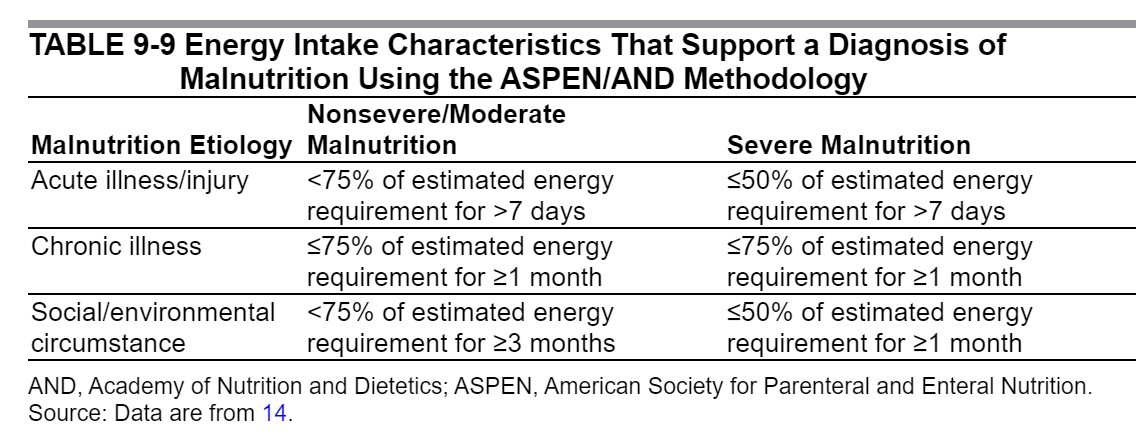
"White JV, Guenter P, Jensen G, et al. Consensus statement: Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition: characteristics recommended for the identification and documentation of adult malnutrition (undernutrition). JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2012;36(3):275–283." FROM-Adult Nutrition Support Core Curriculum, Third Edition, 9. Malnutrition Screening and Assessment
Nutritional Intake
It is common to find aversions to protein foods and vegetables for much of the first trimester, if not longer. Even when women can eat, it might be less than healthy foods with little variety. This can cause guilt and frustration, as well as significant nutritional deficiencies. Women should be reassured and encouraged to make the best decisions possible but focus on increasing fluid and calorie intake any way possible.
A dietary consult can sometimes be helpful, especially for tips on creative inclusion of nutritional foods or increasing calories with nutrient dense foods (e.g. peanut butter).
Nutritional Assessment
For most women with HG, intake of adequate food and fluids is practically impossible for weeks or even months. Standardized nutritional assessment tools are not scaled for pregnant women, yet many women with HG would still show severe risk of malnutrition. However, less than 20% of women get nutritional support.
Importantly, mothers with poor nutritional intake for more than 10 days, weight loss exceeding 15% of preconception weight, electrolyte loss, and low serum magnesium levels are at high risk for refeeding syndrome. Methodical and gradual initiation of nutritional support, starting at 25% of needed nutrition and slowly increasing to goal as tolerated at a controlled rate, is imperative to prevent severe electrolyte and fluid shifts that can be life-threatening.
Monitoring
Daily monitoring of laboratory results, such as phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, calcium, glucose, and potassium, are important over the first week of refeeding. Close monitoring should be continued for at least 10 days, or until electrolytes are stable.
Nutritional Therapy
Being pregnant, women are in a state of accelerated starvation, meaning the adverse effects of starvation occur more quickly. Significant malnutrition can occur as many nutrients are depleted in a relatively short time frame, especially water-soluble vitamins, such as thiamin. Within just 2 weeks, nutritional deficiencies (e.g., B1) can cause neurological and cardiac symptoms that may be fatal. If HG is left untreated, numerous complications can result.
Offsite Research: PubMed Research on Nutrition and HG
Neurological Complications Due to Malnutrition
Neurological Conditions like Wernicke's Encephalopathy and Central Pontine Myelinolysis may be prevented in most cases by careful and proactive repletion of micronutrients. They may be fatal for the mother and unborn child if left untreated. Increasing numbers of cases are being reported each year. Symptoms differ in non-alcoholic patients like mothers with HG.
Our Case Study on HG and WE/CPM/EPM
Find recommendations on identification, prevention and treatment.
WE is typically identified by the symptom triad of ataxia, confusion and oculomotor abnormalities. However, 10-47% of patients lack these signs, especially with ... non-alcoholic [HG] patients... Persistent or prolonged vomiting, confusion, and unintentional weight loss are red flags indicating a high risk of WE. Additional WE signs ... include weakness, dysarthria, confabulation, akinetic mutism, aphasia, cardiac failure, seizures, abdominal pain and nausea. Mental status changes are nearly universal and exhibited as dizziness, drowsiness, apathy, and cognitive impairment. Gait abnormalities range from weakness to inability to stand...