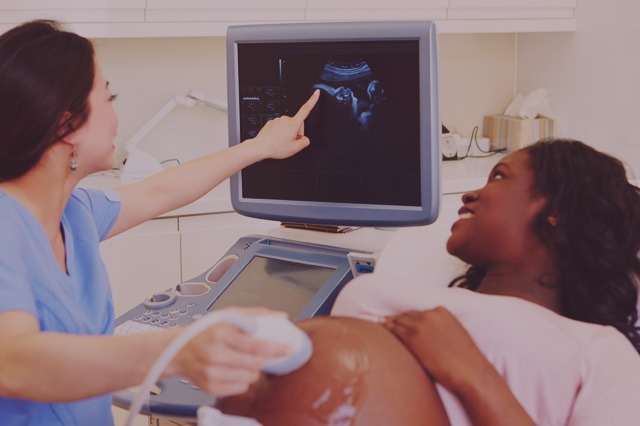
Concerns Over Fetal Defects From Zofran (Ondansetron) Use During Pregnancy
We have received questions expressing concern over the allegations of harm and lawsuits against the manufacturer of Zofran (generic is ondansetron), GlaxoSmithKline (GSK). Here are some important facts to know. Please read our Zofran Safety Statement for the most current information.
- No medications are FDA-approved for treating hyperemesis gravidarum.
- Most research studies, large and small, find little if any increase (e.g. 3 in 10,000) in the number of birth defect cases after ondansetron (Zofran) use in early pregnancy.
- Other concerns about Zofran safety involve giving a large, single dose (32 mg IV) or multiple serotonin antagonist meds simultaneously, neither of which are usually prescribed for HG.
- About 3% of all babies in the US are born with major birth defects and 70% of pregnant women take at least one prescription medication during pregnancy.
- About 15% of over 2.3 million pregnancies take Zofran during pregnancy. (Taylor, 2017)
- Fetal anomalies such as septal defects and orofacial clefts are associated with genetic mutations, maternal diabetes, poor prenatal nutrition/weight gain, and high maternal weight prior to pregnancy.
- Congenital cardiac defects affect 1% of all births and are defined as structural heart problems present at birth and are believed to occur before 10 weeks gestation. They range from minor (septal) to complex. Research finds the risk of cardiac defects (septal) in babies exposed to Zofran to be small or not existent.
- Prematurity and other health problems associated with HG and resulting malnutrition may necessitate greater medical care and thus subsequent diagnosis of more cardiac septal defects in children.
- Cleft defects are structural defects of the mouth, and a common birth defect affecting up to 12 per 10,000 infants. A few studies find a very small increase in the incidence of oral clefts after use of Zofran.
- Research finds lower termination rates with medication usage for HG, suggesting many babies born to HG mothers would not be here without medications that effectively minimize nausea and vomiting.
- GSK did not market Zofran for HG. The 2012 settlement GSK accepted to avoid further litigation focused on 3 other drugs. Zofran's small contribution to the settlement reimbursed the US government for health care charges arising from the use of Zofran off-label. The MDL lawsuit is being dismissed.
- When thinking about risk, it is important to consider that the small potential for increased risks of birth defects found in a few studies on ondansetron are much lower than the risk, for example, of miscarriage after an amniocentesis (which occurs in 1 in 200 to 1 in 400 cases). Few studies consider malnutrition as a cause and thus compare the rates of defects in HG without ondansetron vs HG and ondansetron. Further, the risks from malnutrition, chronic dehydration, or termination of a wanted pregnancy are higher than the possible small risks with medication usage.
- Another weakness in many studies is that we do not know the exact week of exposure, and in some, if the prescribed medication was actually taken. If patients are concerned about the as yet unconfirmed risk, they may want to wait until after 9-12 weeks gestation before starting ondansetron treatment.
Maternal Safety of Ondansetron
Do you have questions about Maternal Safety of Ondansetron? Explore insights on Zofran use and cardiac concerns during pregnancy. Addressing misconceptions, the page covers topics like Torsade de Pointes, Serotonin Syndrome, and pharmaceutical trends. Recommendations for Zofran usage, risks versus benefits, and related research studies provide a comprehensive view for informed decision-making in treating Hyperemesis Gravidarum (HG).
"There are numerous limitations in the current literature on ondansetron safety including exposure to the
medication is not limited to sensitive windows of organogenesis, there is a lack of information on dosing and
compliance, self-reports of exposure are commonly used, an inadequate accounting exists for other factors that may explain the relationship between ondansetron exposure and the adverse outcome, and there exists a lack of biologic plausibility by which ondansetron might cause harm. It is the authors' opinion that current data do not support a reluctance to treat women with ondansetron in clinical practice."
Obstet Gynecol. 2016 May;127(5):873-7.
Oral clefts - unexposed to Zofran 11/10,000 pregnancies
Oral clefts - exposed to Zofran 14/10,000 pregnancies
New England Journal of Med 2013;368:814-23.
- 1970 Mothers who took Zofran during the first trimester in Denmark.Receipt of ondansetron was NOT associated with:
- significantly increased risk of spontaneous abortion
- significantly increased risk of stillbirth
- any major birth defect, preterm delivery, delivery of a low-birth-weight infant, or delivery of a small-for-gestational-age infant.
- “Ondansetron taken during pregnancy was not associated with a significantly increased risk of adverse fetal outcomes.”
BioMed Research International. 2013;2013:909860.
- 251 Mothers who took Zofran during pregnancy in Western Australia, 2002–2005.
- “Our study did not detect any adverse outcomes from the use of ondansetron in pregnancy...”
Reproductive Toxicology. 2014 Dec;50:134-7.
- 1349 Infants of women who took ondansetron in early pregnancy between 1998-2012 in Sweden.
- “No statistically significantly increased risk for a major malformation was found… The teratogenic risk with ondansetron is low but an increased risk for a cardiac septum defect is likely.”
- Note: There were 17 septum (cardiac) defects out of 1349 (~1%) women exposed to Zofran (aka cases) compared to their control group where 315 septum defects were identified out of 41,388 (<1%) pregnancies exposed to meclizine. In both cases and controls approximately 99% of exposed babies did NOT have a cardiac septum defect. Further, only 899 women were exposed during the time required to impact heart development.
Birth defects research. Part A, Clinical and molecular teratology. 2012 January;94(1): 22–30.
- 514 Mothers who took Zofran in United States.
- “Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy was not observed to be associated with an increased risk of birth defects, but possible risks related to three treatments (i.e. proton pump inhibitors, steroids and ondansetron), which could be chance findings, warrant further investigation.”
- Note: The increased risk was very small statistically.
Reproductive Toxicology 62 (2016) 87–91.
- 771 Mothers who took HG worldwide. (Unlike most studies, these mothers reported taking Zofran, not just receiving a prescription for it. Other studies have no verification if a mother actually took their medications.)
- Ventricular septal defects were reported in 2/952 of infants in the HG/Ondansetron-exposure group and 4/1286 in the No HG/No Ondansetron-exposure group. Cleft palate was reported in 1/952 live births in the HG/Ondansetron and 2/1286 in the No HG/No Ondansetron-exposure groups.
- Women with a history of HG who took ondansetron reported fewer miscarriages and terminations, and higher live birth rates. The overall results do not support evidence of teratogenicity ofondansetron.
Obstet Gynecol. 2016 May;127(5):878-83.
- A Systematic Review of recent studies. The 3 largest studies showed no risk of defects. The small risk in a few studies was not seen in the larger studies.
- The overall risk of birth defects associated with ondansetron exposure appears to be low. There may be a small increase in the incidence of cardiac (septal defects) abnormalities...
Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Aug;132(2):385-394.
- A review of 51 defects using data from two case-control studies with 628 women taking Zofran in 1st trimester.
- "For the majority of specific birth defects investigated, there was no increased risk associated with first-trimester use of ondansetron for treatment of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy compared with no treatment" and there a possible chance finding of associations with cleft palate and renal agenesis-dysgenesis."
J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2018 Jul;40(7):910-918.
- Systematic review of 10 studies. Sample sizes ranged from 17 to 1 501 434. Systematic review finds studies do show evidence for fetal harm.
- "Our results highlight the paucity [lack] of evidence linking prenatal exposure to ondansetron to an increased risk of congenital malformations."